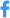
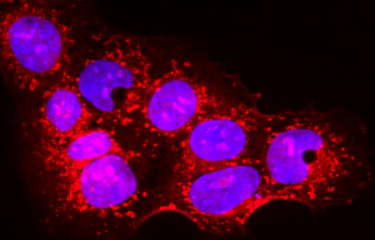
The main cause of death in patients suffering from cystic fibrosis is respiratory infection caused by different bacterial populations, which vary according to the age of the patient. Scientists at the Institut Pasteur and Inserm have identified a novel mechanism used by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium to hijack the immune system of its host in order to eradicate another bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus ("golden staph"), and take its place in airways.