Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is a gene whose mutations are associated with a rare, hereditary form of colorectal cancer known as familial adenomatous polyposis. Research led by scientists at the Institut Pasteur, CNRS and Inserm have recently demonstrated that mutations to this gene do not only lead to the emergence of colon polyps; they also harm the immune system, leaving it unable to tackle inflammation of the colonic mucosa. This dual impact supports the development of cancer. The finding, published in the journal Cell Reports on October 3rd, 2017, advances scientific knowledge on the development mechanisms of colorectal cancer.
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition characterized, from puberty, by the formation of a very large number of polyps, small growths on the inner surface of the colon and the rectum which can develop into tumors. If left untreated, these polyps may result in colorectal cancer before the age of 40.
Colon cancer is one of the most deadly forms of cancer, and familial adenomatous polyposis currently represents 1% of all cases of colorectal cancer. Those affected by this hereditary disease therefore need close medical supervision.
Research led by scientists from the Institut Pasteur, CNRS and Inserm recently demonstrated that mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene, known to be involved in familial adenomatous polyposis, do not only lead to the emergence of colon polyps; they also harm the immune system, leaving it unable to tackle inflammation of the colonic mucosa. This dual impact may favor the development of cancer.
As Andrés Alcover, Head of the Lymphocyte Cell Biology Unit at the Institut Pasteur and last author of the paper, explains, "the APC protein, associated with the microtubule cytoskeleton, has a major effect on the structure and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells. By disrupting these functions in intestinal cells, APC mutations can lead to the development of tumors."
Scientists already knew that APC mutations could influence the immune system, but they had not yet identified the molecular mechanisms involved and the link with colorectal cancer development. The teams of scientists elucidated how the APC protein activates a particular type of immune cell known as T lymphocytes. "The protein activates T lymphocytes using a factor known as NFAT[1]," continues Andrés Alcover. "Polyposis patients have a mutant version of the gene, which leads to a deficiency in APC protein and could reduce the presence of NFAT in cell nuclei" – thereby preventing lymphocyte activation.
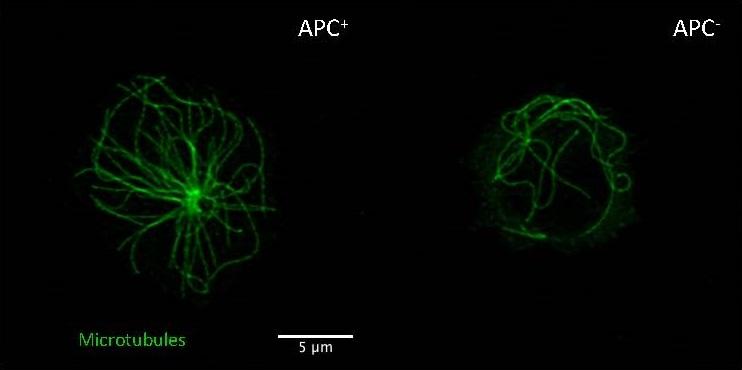
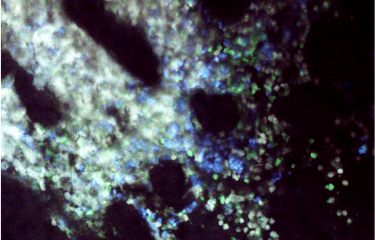
Human T lymphocytes expressing or lacking APC. Lack of APC impairs microtubule cytoskeleton organization (green filaments). © Institut Pasteur
One family of T lymphocytes, known as regulatory T cells, is particularly sensitive to APC mutations. The scientists observed a dysfunction in these regulatory T cells – which are present in large numbers in the intestine – in mice with these mutations that are predisposed to develop polyposis like the patients. This dysfunction leads to a deregulation of the immune system in the intestine and a failure to control local inflammation. "This is the first time that we have characterized at molecular level how mutations in the APC protein affect the immune system, creating favorable conditions for cancer development", emphasizes Andrés Alcover.
These findings suggest that mutations in the APC gene play a dual role in the development of colorectal cancer. Not only do they trigger the development of polyps; they also reduce the action of the immune system, preventing it from controlling gut inflammation. This vicious circle supports the development of cancer.
It remains to be seen whether defects in the APC protein in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis have consequences for the other cells in the immune system, especially those that directly eliminate cancer cells. If so, this research might pave the way for the development of new therapies to improve the efficacy of treatment for patients with familial adenomatous polyposis or other forms of intestinal cancer.
[1] NFAT: nuclear factor of activated T cells.
This project was funded by the ARC Foundation for Cancer Research, the Institut Pasteur, Inserm, the ANR, NIDDK-USA and the People Programme (Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions) of the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-2013/ under REA grant agreement no. 317057 HOMIN-ITN.
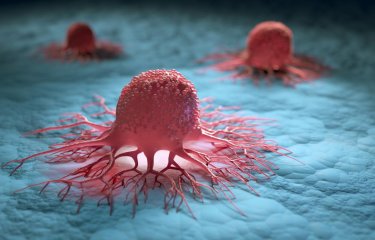
Photo: Immune system attack on a tumor. Left-hand image: in mice, when certain immune system killer cells (T lymphocytes, in red) are injected in the bloodstream they enter the tumor (in yellow). Right-hand image: after a few days the killer cells have destroyed the cancer cells, as observed in this model.
Source
* Adenomatous polyposis coli defines Treg differentiation and anti-inflammatory function through microtubule-mediated NFAT localization, Cell Reports, October 3, 2017
Sonia Agüera-González (1,2,3,5), Oliver T. Burton (4,8), Elena Vázquez-Chávez (1,2,3), Céline Cuche (1,2,3), Floriane Herit (1,2,3,6), Jérôme Bouchet (1,2,3,6), Rémi Lasserre (1,2,3,7), Iratxe del Río-Iñiguez (1,2,3), Vincenzo Di Bartolo (1,2,3), Andrés Alcover (1,2,3)
1. Institut Pasteur. Department of Immunology. Lymphocyte Cell Biology Unit.
2. CNRS URA1961.
3. INSERM U1221. 75015 Paris, France.
4. Division of Immunology, Boston Children's Hospital and Department of Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
5. Institut Curie. Membrane and Cytoskeleton Dynamics Group, CNRS UMR144, 75005 Paris, France.
6. Institut Cochin, INSERM, U1016, CNRS, UMR8104, Paris Descartes University, Sorbonne Paris Cité, 75014 Paris, France.
7. Marseille-Luminy Immunology Center (CIML), Aix Marseille University UM2, Inserm, U1104, CNRS UMR7280, 13288 Marseille, France.
8. Department of Microbiology and Immunology, VIB-University of Leuven, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.020