Causes and origins
Cystic fibrosis is a fatal recessive genetic disorder (both parents must carry the defective gene to pass on the disease). The gene responsible for cystic fibrosis encodes a protein known as cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), which was discovered in 1989. More than 2,000 mutations have been identified to date, of which the most frequent (found in about 80% of patients in France) is the F508del. A mutation in the CFTR channel modifies the ionic exchanges and makes the body produce abnormally high quantities of thick, sticky mucus. Although the disorder affects the mucus produced by several organs, impairment to the respiratory system is the main cause of morbidity and mortality.
Symptoms
The excess of mucus and the lack of mucociliary clearance (a mechanism by which any particles inhaled that are larger than a certain size are transported to the digestive tract) encourage the development of respiratory infections by opportunistic bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Hemophilus influenzae). These infections cause an exacerbated inflammatory response in the airways which becomes chronic, destroying lung tissue and leading to a progressive loss of respiratory function until the patient dies.
Cystic Fibrosis and Covid-19
One year after the start of the Covid-19 epidemic, reliable and growing data are accumulating about cystic fibrosis patients, who have contacted Covid-19, in different countries. Most adults and children with cystic fibrosis who have contracted this coronavirus recover in the same way as people without cystic fibrosis. The Covid-19 that these patients contracted was ultimately less severe than was assumed at the beginning of the pandemic. It should be noted, however, that patients with severely impaired lung function, complications such as diabetes, or who have undergone lung transplantation are more likely to be hospitalized, and sometimes in the ICU.
However, it should be kept in mind that the low number of cases of infection by the Covid-19 virus in patients with cystic fibrosis seems to be related to the control of barrier procedures that these patients use in many circumstances outside of any epidemic context, since their youngest age.
Epidemiology
Cystic fibrosis affects approximately one in every 2,500 births in Europe and North America. About 4% of the general Western population are healthy heterozygous carriers of the disorder (individuals with one defective and one normal copy of the gene). The prevalence of cystic fibrosis varies worldwide, with very few cases in Africa and Asia. The prevalence in Europe is estimated at around 8 to 12 cases for every 100,000 inhabitants. Since 2002, France has carried out systematic newborn screening. The incidence varies according to region, from 1/2,500 in north-western France to 1/10,000 in the south-east. There are around 2 million heterozygous carriers in the country.
Treatments
There is currently no curative treatment for cystic fibrosis, but considerable progress has been made in terms of available therapy, improving both quality of life and life expectancy (estimated at 47 years in 2005 in France, compared with just 7 years in 1965). Treatment is symptomatic and requires coordination between several specialists: pediatricians, physiotherapists, dietitians and psychologists. It mainly involves addressing respiratory problems, although digestive and nutritional management also plays an important part.
There are two main aims of respiratory therapy: improving mucociliary clearance and reducing bacterial lung infections. Treatment involves respiratory physiotherapy, antibiotic therapy, and the use of bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs and mucolytics. A lung or heart and lung transplant may be performed in some cases. Despite several trials, gene therapy has not yet lived up to its promise. Antibiotic therapy can sometimes be ineffective because of the development of multi-drug-resistant bacterial strains in patients' lungs and also because antibiotics are hindered by the thick layer of mucus.
Since the years 2015-2018, "new therapies" targeting dysfunctions related to certain CFTR mutations (modulatory or corrective treatments) have significantly improved the symptoms of the disease. The results of these studies are impressive: all report a significant, and for some, dramatic decrease in all cystic fibrosis-related symptoms and disorders, particularly respiratory manifestations. Subsequent studies have been able to extend pharmacological treatments of the CFTR channel to the majority of CFTR mutations.
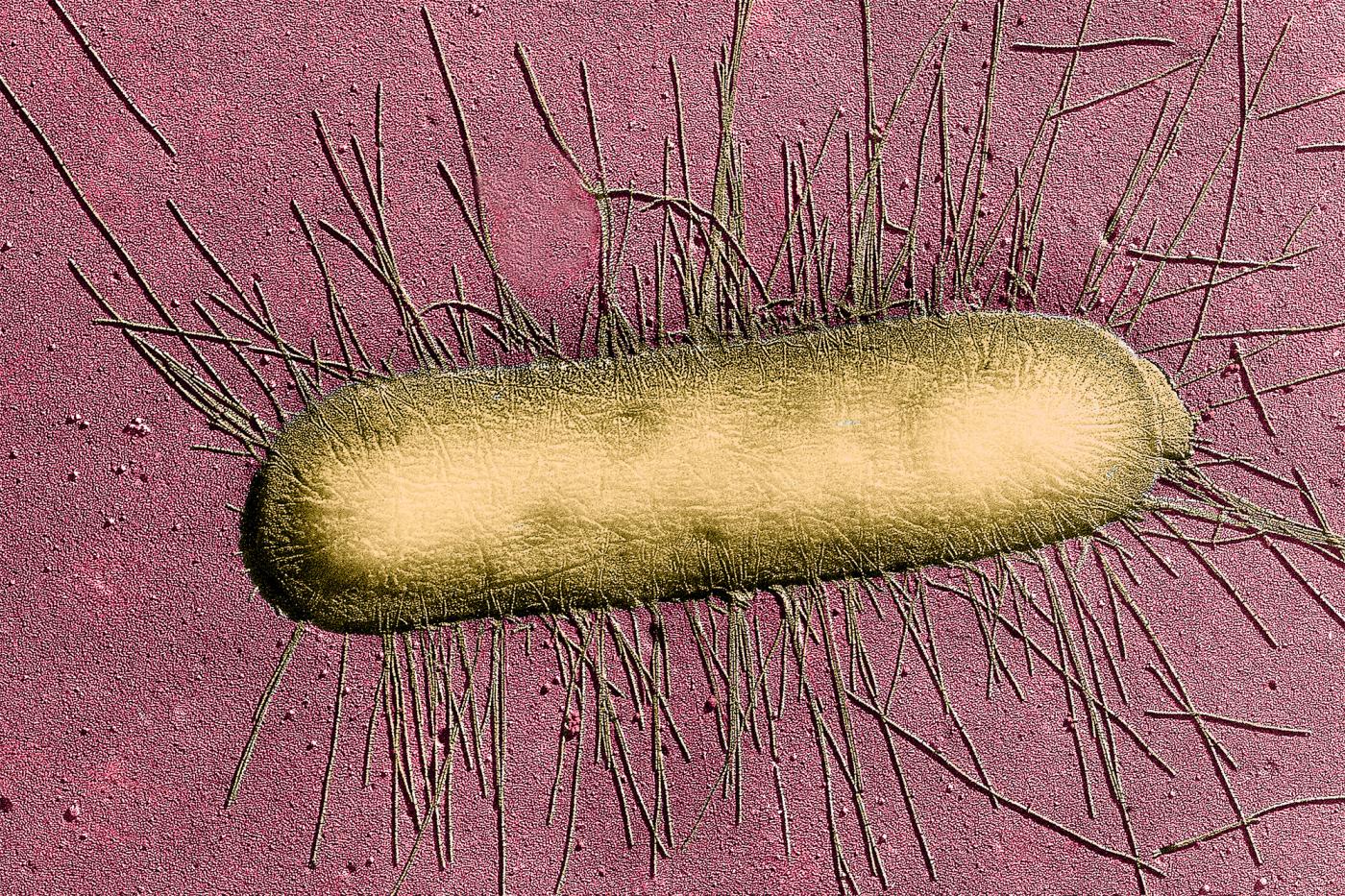
News weapons to fight bacteria
June 2021
The following Foundations have contributed to the funding of our research: